What is it?
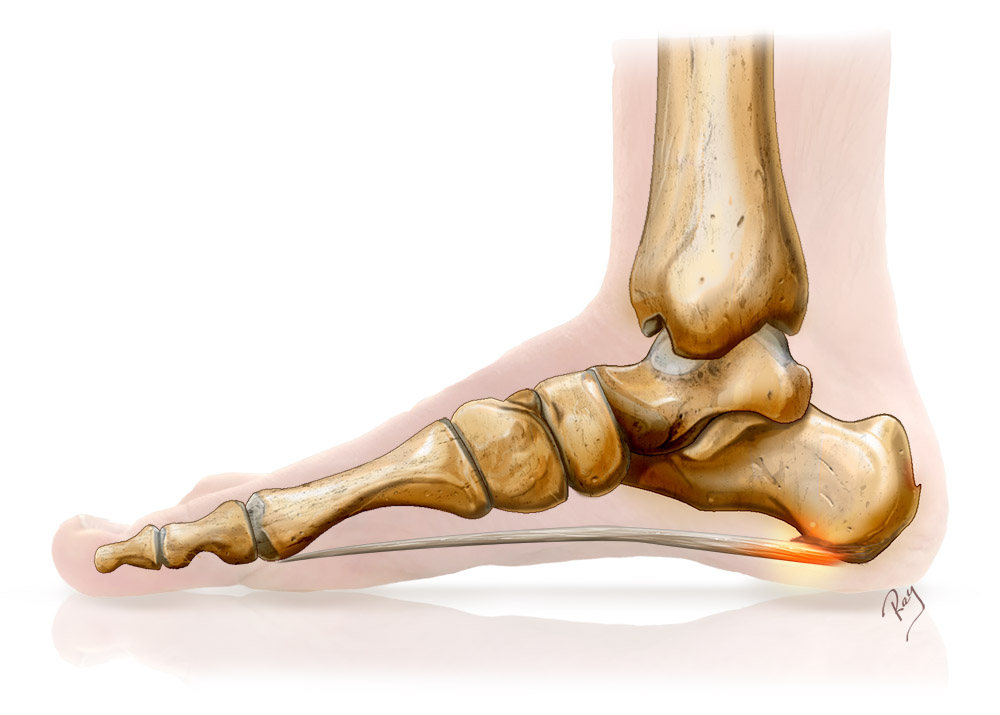
Plantar fasciitis, also known as plantar aponeurosis or a heel spur, is a painful condition affecting the plantar area of the heel. It is the primary cause of talagia or heel pain. It is an inflammation of the plantar fascia – a fibrous band of tissue extending from the calcaneus to the toes and involved in the arched shape of the foot. Like many tendon disorders, it results from a repetitive strain injury.
Over time, a heel spur will often develop. This heel spur is, in fact, a calcification of the plantar fascia and reflects the chronic nature of the condition. The name erroneously suggests that the spur is the main cause of pain while it actually reflects a more serious condition whose discomfort can at times be extremely disabling. The condition is mainly caused by degenerative ligament damage.
There are many causes for this condition; however, it is generally associated with a shortening of the posterior structures (i.e. the calf muscles). The anatomical and mechanical link between the posterior muscles and the fascia result in chronic overloading at its insertion point, causing local micro-lesions and ultimately pain.
Being overweight, wearing unsuitable shoes, repeatedly walking on hard floors, chronic systemic inflammations, having flat feet/high arches or sports injuries are other possible causes of fasciitis.