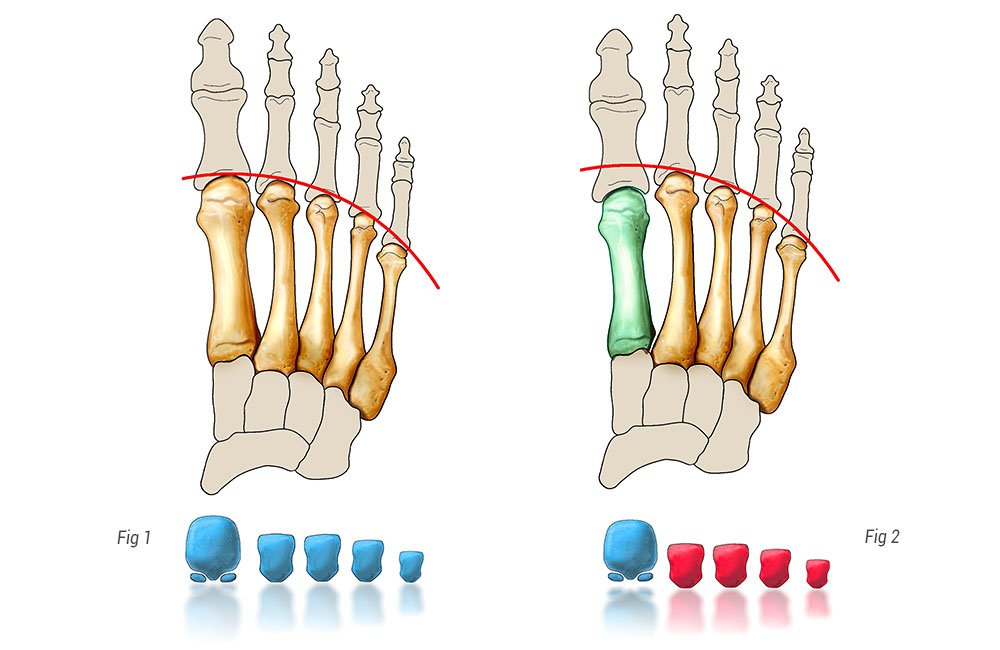
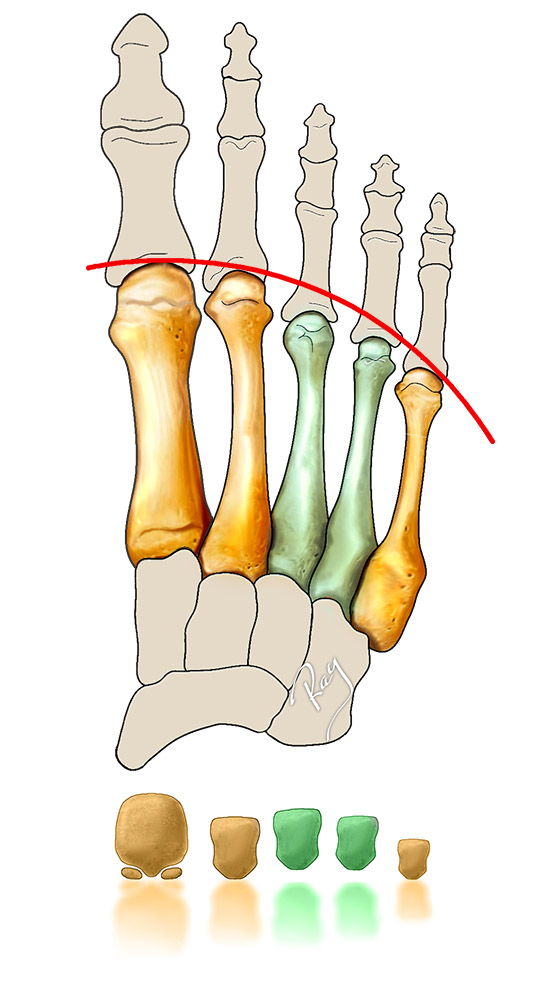
What is it?
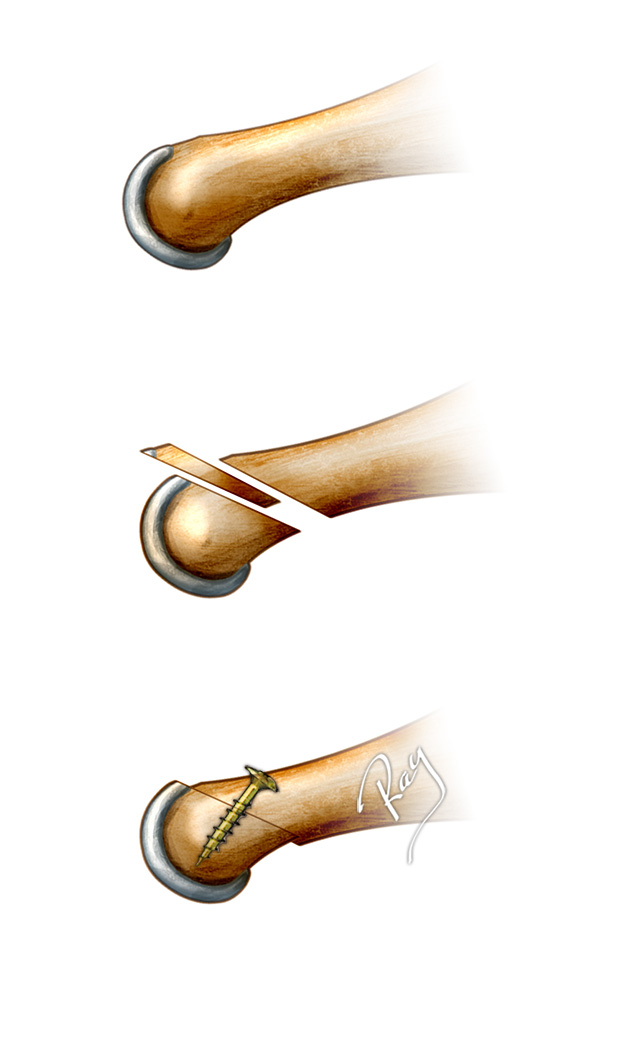
Metatarsalgia is pain located under the forefoot. It has many causes and a specific clinical examination usually determines its aetiology and a targeted treatment can then be proposed.
The body’s weight is distributed between the five metatarsals (bones in the midfoot, linking with the toes). The first bone, linked to the big toe, receives 2.5 times more weight than the others. The rest of the weight is then divided among the other metatarsals. Any imbalance of this relationship causes a cascading change meaning that an extra burden falls onto one or more of the other metatarsals. Pain then develops specifically under the overburdened metatarsals.