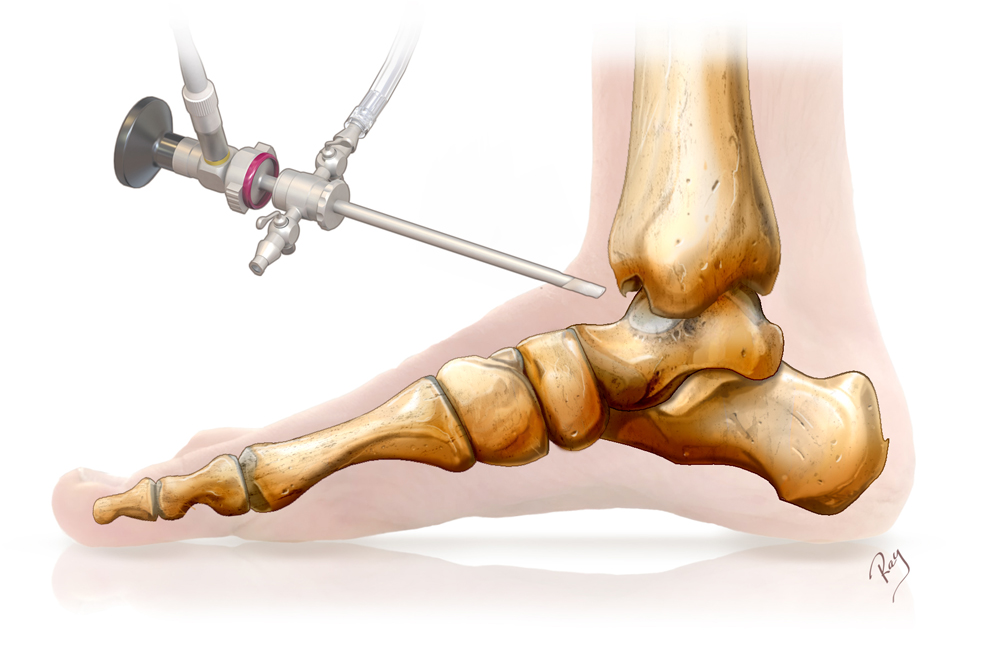
Arthroscopic surgery was first used at the beginning of the last century and the technique was popularised in the 1970s for the treatment of knee conditions. It rapidly emerged as a reliable and effective tool for orthopaedic surgery. The development of techniques has helped adapt it to other joints like the shoulder, hip, elbow and ankle.
The surgery involves inserting a camera into a joint through an incision of less than one centimetre in size. One or more other incisions are made to allow the use of other specific instruments and tools. The camera (the arthroscope) allows a complete exploration of the area around the joint, which is usually impossible in open surgery. In addition, the minimally-invasive approach limits the surgical aggression and allows faster recovery times than conventional surgery.